4 Encoding And Evolution
Formats for encoding data
Programs work with 2 different representations of data
- In-memory data (using list,arrays, hash tables, trees)
- Writing it to a file / sending it over network (encoding it using JSON etc)
JSON, XML and Binary Variants
- JSON, XML, CSV popularly used language independent formats
- Textual formats
Problems with JSON, XML, CSV
- XML, CSV cannot differentiate a number and a string
- JSON cannot differentiate integers and floating point numbers
- No support for binary strings (hacky alternative base64 is used for encoding)
Binary Encoding
- JSON, XML uses significantly more space compared to binary formats
- Binary formats: MessagePack, BSON, BJSON, UBJSON, BISON
- binary formats supports more set of datatypes like integers,float, binary strings
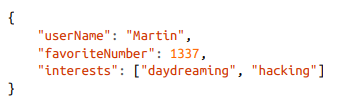
Ex: encoding a json data using MessagePack binary encoding
JSON
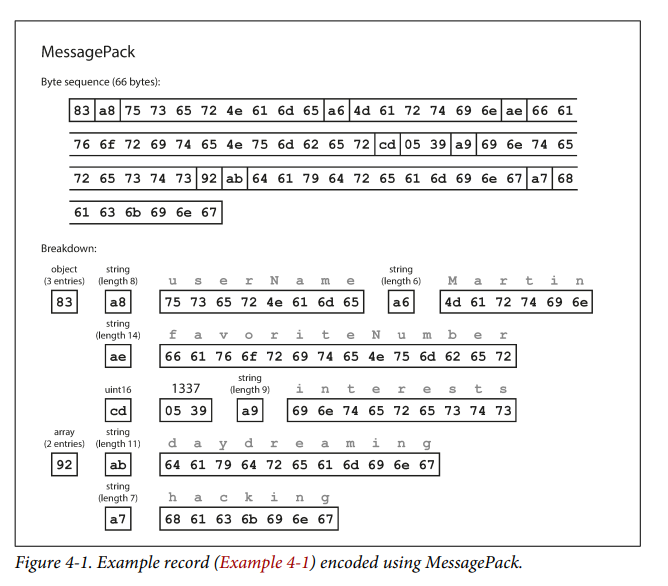
Binary Encoding
Thrift and Protocol Buffers
- Protocol Buffers - by Google
- Thrift - by Facebook
IDL - interface definition language
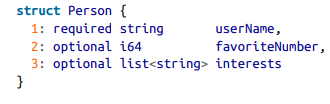
IDL for Thrift:
IDL for Protocol Buffers:

Both comes with a code generation tool for converting the schema definition to specific language code
Thrift and Protocol buffers doesnt encode field tag names but use the field id number to connect the field value to tag
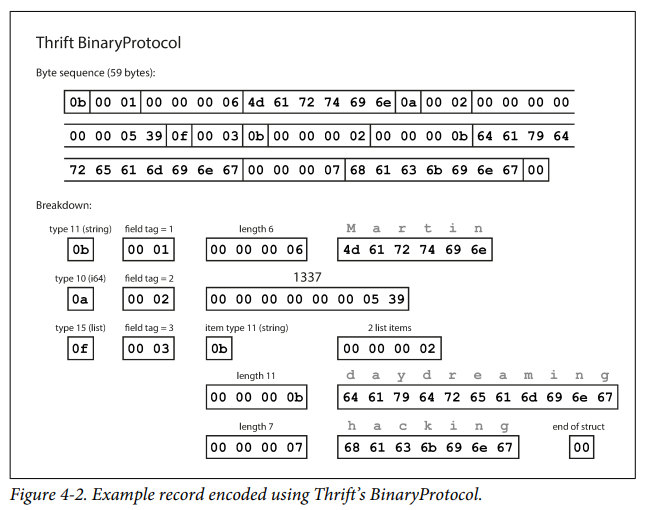
Thriftt uses 2 types of binary encodings
Binary Protocol
Compact Protocol
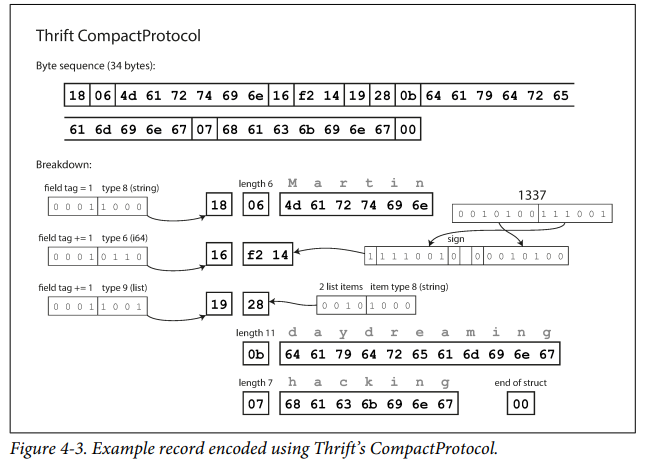
Protocol buffers' encoding scheme is similar to compact Protocol of thrift.
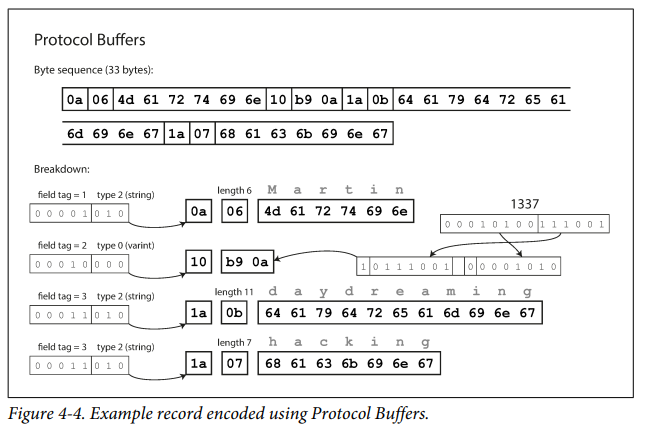
- Field being optional / required doesn't make any difference in the encoding. It is checked during runtime.
Field Tags and Schema Evolution
- Field tags play a major role.
- For any field name updation - no issues as encoding maps field tag --> field name
- When new field is inserted, it is given a new field tag. Some applications using older version of schema wont even read this.
- Only thing to ensure backwards compatibility is to not make a newly inserted field required.
Modes of DataFlow
- Via Databases
- Via service calls
- Via asynchronous message passing
Dataflow through databases
- Process that writes to db encodes it
- Process that reads from db decodes it
- Should support forward and backward compatibility
- New fields should be preserved even though an older outdated application rewrites the data in an older format
Dataflow Through Services: REST and RPC
Web Services - service communication is done using HTTP
Ex: microservices talking to each other, native app making an AJAX req.
REST
- A philosophy rather than a protocol
- Simple data formats using URLs, using HTTP features for cache control, auth and content negotiation
SOAP
- XML based protocol for making network API requests.
- Not so good, skippinggggg
Problems with RPCs
- RPC model tries to make a request to a remote network service look the same as calling a function or method in your programming language, within the same process.
- Local function call is predictable whereas network call is unpredictable to succeed.
- Network function is much slower than a local function call
- Client and server maybe in diff languages, so RPC framework has to do the translation process between them.
Current directions of RPC
- gRPC uses protocol buffers, Finagle uses Thrift, rest.li uses JSON over HTTP
- Finagle and Rest.li use futures (promises) for asynchronous function calls.
- gRPC supports streams wherein a series of requests and responses can be made in a call.
Message Passing Dataflow
- Uses a
message brokerinbetween 2 services to asynchronously pass the messages - Has several advantages over plain RPC
- message broker can act as buffer if recipient is unavailable / overloaded
- automatically redeliver messages
- sender needn't know IP addresses
- allows one message to be sent to several recipients
- Sender doesn't expect response from the recipient
Message Brokers
- RabbitMQ, ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka - examples
- Flow : one process sends the message to queue, broker ensures message is delivered to one or more consumers
- No particular data model
Distributed Actor Frameworks
- Actor model - Programming model for concurrency within single process
- Logic is encapsulated with
actorsrather than threads which has issues like race conditions and deadlocks - Each actor represents one client or entity and may have a local state (not shared by any other actors)
- Actors communicate with each other through message passing
- Actors process only one message at a time, neednt worry about threads and can be scheduled independently by the framework
- Read more about actor model link
- Same message passing mechanism is used in distirbuted actor frameworks
- Popular frameworks which uses actor model
Akkauses java inbuild serialization by defaultOrleansuses custom data encoding formatErlang OTP- very hard to make changes to record schemas